EXIPRAZOLE 20
E.C. capsule Omeprazole 20mg ( contains 28 E.C.Cap )
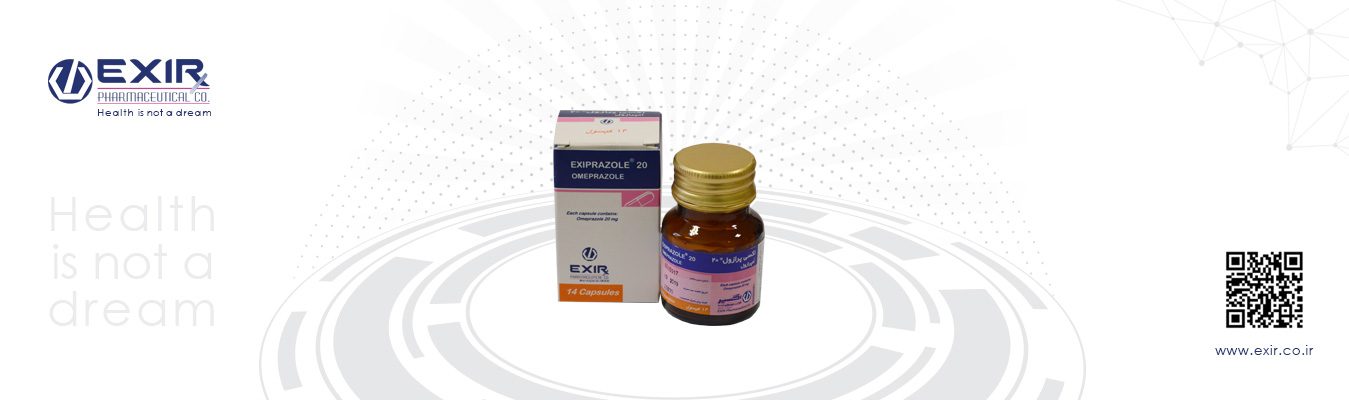
| Generic Name of Product | Brand Name | Dosage Form | Strength | Pharmacologic Group | Therapeutic Group | Unit Per Pack |
| Omeprazole | Exiprazole | Capsule | 20 mg | Proton pump inhibitor | ointestinal agents | 28 |
Indications And Usage | Omeprazole capsules are indicated in: Adults
• Treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome |
Administration | It is recommended to take Exiprazole capsules in the morning, swallowed whole with half a glass of water. The capsules must not be chewed or crushed. For patients with swallowing difficulties and for children who can drink or swallow semi-solid food : Patients can open the capsule and swallow the contents with half a glass of water or after mixing the contents in a slightly acidic fluid e.g. fruit juice or applesauce, or in non-carbonated water. Patients should be advised that the dispersion should be taken immediately (or within 30 minutes) and always be stirred just before drinking and rinsed down with half a glass of water. |
Contraindications | Hypersensitivity to the active substance, substituted benzimidazoles or to any of the excipients Omeprazole like other proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) must not be used concomitantly with nelfinavir |
Precautions | In the presence of any alarm symptom (e.g. significant unintentional weight loss, recurrent vomiting, dysphagia, haematemesis or melena) and when gastric ulcer is suspected or present, malignancy should be excluded, as treatment may alleviate symptoms and delay diagnosis. |
Adverse Reactions | headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, gas (flatulence), dizziness, upper respiratory infection, acid reflux, constipation, rash, cough. |
Pregnancy and lactation | Pregnancy: Results from three prospective epidemiological studies (more than 1000 exposed outcomes) indicate no adverse effects of omeprazole on pregnancy or on the health of the foetus/newborn child. Omeprazole can be used during pregnancy.
Breast-feeding: Omeprazole is excreted in breast milk but is not likely to influence the child when therapeutic doses are used.
|
Renal and liver Impairment | Renal impairment Dose adjustment is not needed in patients with impaired renal function
Hepatic impairment In patients with impaired hepatic function a daily dose of 10–20 mg may be sufficient |
Laboratory Tests | - |